Virtual Control API
Virtual controls provide automation capabilities for unstructured areas on the interface. Combined with image recognition (Image), text recognition (OCR), and general operations (Mouse / Keyboard) technologies, they can be operated and verified in scenarios not recognized by standard automation frameworks.
| API Name | Description |
|---|---|
| all | Get all virtual controls matching the search criteria. |
| click | Click a specified position within the virtual control area. |
| dblClick | Double-click the virtual control area. |
| exists | Determine whether the virtual control exists. |
| highlight | Highlight the virtual control area. |
| moveMouse | Move the mouse into the virtual control. |
| pressKeys | Simulate keyboard input in the virtual control. |
| rect | Get the rectangular area information of the virtual control. |
| takeScreenshot | Capture a screenshot of the virtual control. |
| wheel | Scroll the mouse wheel inside the virtual control. |
| modelImage | Get the reference image saved in the virtual control model. |
| modelProperties | Get the model properties of the virtual control. |
| visualText | Get text in the virtual control via OCR. |
| clickVisualText | Click the specified text recognized in the virtual control. |
| textItems | Get text block child controls segmented in the virtual control. |
| checkImage | Compare the virtual control with a reference image to verify visual consistency. |
The APIs of virtual controls can be roughly divided into three categories:
- Basic Operation API: General methods similar to traditional control operations, used for clicking, double-clicking, existence checking, highlighting, mouse movement, keyboard input, screenshots, etc.
- Text Recognition (OCR) Related API: Extract text from virtual controls via OCR, and perform click operations on the recognized text.
- Image Comparison API: Check whether the current interface of the virtual control is consistent with the expected image via image comparison technology to achieve visual verification.
Type Definition
export interface Virtual {
// Basic Operations
all(): Promise<IVirtual[]>;
click(x?: number, y?: number, mousekey?: number): Promise<void>;
dblClick(x?: number, y?: number, mousekey?: number): Promise<void>;
exists(seconds: number): Promise<boolean>;
highlight(duration?: number): Promise<void>;
moveMouse(x?: number, y?: number, seconds?: number): Promise<void>;
pressKeys(keys: string, opt?: PressKeysOptions | number): Promise<void>;
rect(): Promise<Rect>;
takeScreenshot(filePath?: string): Promise<string>;
wheel(value: number): Promise<void>;
modelImage(options?: {encoding: 'buffer' | 'base64'}): Promise<string | Buffer>;
modelProperties(all?: boolean): {[x: string]: any};
// OCR Related
visualText(options?: { whitespace: boolean }): Promise<string>;
clickVisualText(text: string, options?: {
cache: boolean,
x: number,
y: number,
button: number,
double: boolean,
down: boolean,
up: boolean }): Promise<void>;
textItems(options?: {expand?: number}): Promise<IVirtual[]>;
// Image Comparison Related
checkImage(options?: CheckImageCompareOptions | string): Promise<void>;
}class Virtual:
# Basic Operations
def all() -> List["Virtual"]
def click(x: Optional[int] = None, y: Optional[int] = None, mousekey: Optional[int] = None) -> None
def dblClick(x: Optional[int] = None, y: Optional[int] = None, mousekey: Optional[int] = None) -> None
def exists(seconds: int) -> bool
def highlight(duration: Optional[int] = None) -> None
def moveMouse(x: Optional[int] = None, y: Optional[int] = None, seconds: Optional[int] = None) -> None
def pressKeys(keys: str, opt: Union[PressKeysOptions, int] = None) -> None
def rect() -> Dict[str, int]
def takeScreenshot(filePath: Optional[str] = None) -> str
def wheel(value: int) -> None
def modelImage(options: Optional[Dict[str, str]] = {'encoding': 'base64'}) -> Union[str, bytes]
def modelProperties(all: Optional[bool] = False) -> Dict[str, Any]
# OCR Related
def visualText(options: Optional[Dict[str, bool]] = None) -> str
def clickVisualText(text: str, options: Optional[Dict[str, Union[bool, int]]] = None) -> None
def textItems(options: Optional[Dict[str, int]] = None) -> List[Virtual]
# Image Comparison Related
def checkImage(options: Optional[any] = None) -> None
1. Basic Operation API
The usage of these methods is similar to general control operations in Qt or Windows automation, please refer to:
- Qt Common Control Operations
- Windows Common Control Operations
- ATK Common Control Methods
- Java Common Control Methods
Main APIs are as follows:
all(): Get all matching results conforming to the current virtual control definition, returning an array of virtual controls.click/dblClick: Click or double-click a specified position within the virtual control (coordinates are optional, defaults to control center if not passed).exists(seconds: number): Check if the virtual control exists within the specified seconds.highlight(duration?: number): Highlight the virtual control to assist debugging and locating.moveMouse(x?, y?, seconds?): Move the mouse to a point within the virtual control.pressKeys(keys, options?): Simulate keyboard input in this control.rect(): Get the rectangular area information of the virtual control.takeScreenshot(filePath?): Capture a screen image of the current area of the virtual control.wheel(value): Scroll the mouse wheel within the virtual control area.modelImage(options?): Get the reference image saved in the model for this virtual control (Base64 or Buffer).modelProperties(all?: boolean): Get model properties of the virtual control (such as alignment, rectangular area, etc.).
2. OCR Related API
When text controls in the interface cannot be directly recognized, text can be extracted from virtual controls through OCR, and click operations can be performed based on the text. For more OCR principles and details, please refer to Optical Character Recognition (OCR).
visualText(options?: {whitespace: boolean})
Perform OCR recognition on the image within the virtual control area and return the recognized text string.
Parameters:
- options: (Optional) Recognition options
- whitespace:
booleantype, specifies whether to recognize spaces, default isfalse.
- whitespace:
Returns:
Promise<string>- Returns the text content in the picture.
Sample Code
let text = await model.getVirtual("Virtual1").visualText();
console.log('Recognized Text:', text);text = model.getVirtual("Virtual1").visualText()
print('Recognized Text:', text)clickVisualText(text: string, options?: {cache: boolean, x: number, y: number, button: number, double: boolean, down: boolean, up: boolean})
Use OCR to find specified text in the virtual control and click on that text area.
Parameters:
- text:
string- The text to look for (e.g., "Open"). - options: (Optional)
objecttype, options for text clicking.- cache:
booleantype, sets whether to cache recognition information, default isfalse. When set totrue, the last OCR result will be reused, thereby improving the response speed of subsequent clicks on other text within the same control. - x:
numbertype, horizontal offset (pixels) of the click position relative to the top-left corner of the text area.0indicates clicking the horizontal center of the text area. Default value is0. - y:
numbertype, vertical offset (pixels) of the click position relative to the top-left corner of the text area.0indicates clicking the vertical center of the text area. Default value is0. - button:
numbertype, indicates the mouse button to use,1is left button,2is right button, default value is1(Left). See identifying keys table in Mouse Keys Enum. - double:
booleantype, when set totrue, double-click the mouse button at the target canvas position, default isfalse. - down:
booleantype, press the mouse button (without releasing) at the target canvas position, default isfalse. - up:
booleantype, release the mouse button at the target canvas position, default isfalse.
- cache:
Returns:
- An asynchronous method that returns no value.
Sample Code (Reuse OCR Cache Info)
The following example demonstrates how to use the cache option. Taking Windows Calculator as an example, recognize the number pad of the calculator and add it to the model with the object name "Number pad".
(async function () {
let numPad = model.getGeneric("Number pad").getVirtual();
await numPad.clickVisualText('4', { cache: true });
await numPad.clickVisualText('5', { cache: true });
await numPad.clickVisualText('6', { cache: true });
})();numPad = model.getGeneric("Number pad").getVirtual()
numPad.clickVisualText('4', { 'cache': True })
numPad.clickVisualText('5', { 'cache': True })
numPad.clickVisualText('6', { 'cache': True })Sample Code (Double Click Specific Position of Text in Virtual Control)
The following example demonstrates how to use x, y and double options. In this example, the visual area of the text ABC on the virtual control named virtual will be located, and then the mouse will perform a double-click operation at the position horizontally offset by 30 pixels and vertically offset by 20 pixels from the top-left corner of the visual area.
model.getVirtual("virtual").clickVisualText("ABC", { x: 30, y: 20, double: true });model.getVirtual("virtual").clickVisualText("ABC", { 'x': 30, 'y': 20, 'double': True })Sample Code (Right Click Text in Virtual Control)
The following example demonstrates how to use x, y and button options. In this example, the visual area of the text XYZ on the virtual control named virtual will be located, and then the mouse will perform a right-click operation at the center position of the visual area.
model.getVirtual("virtual").clickVisualText("XYZ", { x: 0, y: 0, button: 2 });model.getVirtual("virtual").clickVisualText("XYZ", { 'x': 0, 'y': 0, 'button': 2 })Exception Handling
When the given text is not found in the specified control, an exception will be thrown. You can use takeScreenshot() to capture a screenshot and Ocr.getTextLocations() to view the recognized text block information for diagnosis.
(async function () {
let numPad = model.getGeneric("Number pad").getVirtual();
let snapshot = await numPad.takeScreenshot();
let blocks = await Ocr.getTextLocations(snapshot);
console.log(JSON.stringify(blocks, null, 2))
})();textItems(options?: { expand?: number })
Get the list of child virtual controls automatically segmented by text blocks within the current virtual control. Each text block is wrapped as a directly operable Virtual child object (can execute click(), highlight(), takeScreenshot(), etc.).

Parameters
- options.expand (Optional)
numbertype. Used to expand specified pixels in four directions outside the recognized text block rectangular area, default value is2. Appropriate expansion helps improve the accuracy of secondary processing (such as secondary OCR, screenshot, comparison, etc.) in scenarios with blurry font edges, anti-aliasing, or overly thin rendering.Tip: Too large
expandvalue may cause rectangles of adjacent text blocks to overlap. If your subsequent logic is based on "first hit block", please use a smallerexpand(e.g., 2~4) on pages where adjacent items are close.
Returns
- Returns a list of child virtual controls, where each child control corresponds to a visual text block.
Example: Extract Menu Text and Click
// Expand each text block by 4 pixels, click the first "Settings"
const items = await model.getVirtual("menuBar").textItems({ expand: 4 });
for (const v of items) {
const text = await v.visualText(); // Read text of this child block
if (text.trim() === "Settings") {
await v.click(); // Hit area is more tolerant
break;
}
}# Expand each text block by 4 pixels, click the first "Settings"
items = model.getVirtual("menuBar").textItems({ "expand": 4 })
for v in items:
text = v.visualText().strip() # Read text of this child block
if text == "Settings":
v.click() # Hit area is more tolerant
breakExample: Improve Screenshot Accuracy
const items = await model.getVirtual("toolbar").textItems({ expand: 6 });
const saveBtn = items.find(async v => (await v.visualText()).trim() === "Save");
if (saveBtn) {
const snap = await saveBtn.takeScreenshot();
// Compare snap with expected image (omitted)
}items = model.getVirtual("toolbar").textItems({ "expand": 6 })
save_btn = None
for v in items:
if v.visualText().strip() == "Save":
save_btn = v
break
if save_btn:
snap_base64 = save_btn.takeScreenshot()
# Compare with expected image (omitted)
3. Image Comparison API
Through image comparison technology, the checkImage method can compare the current visual representation of the virtual control with an expected reference image. This method is a key tool for visual verification, commonly used to detect control state changes and ensure UI visual consistency.
When running scripts in the CukeTest environment, if the checkImage method fails due to differences exceeding the tolerance, the system will automatically display the difference image in the run output panel and add it as an attachment to the final test report, facilitating direct viewing and problem analysis.
To display difference image thumbnails in the output panel, ensure that
reportStepsis enabled in run settings.
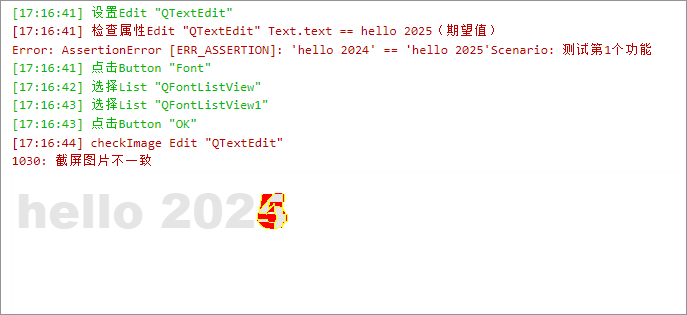
checkImage(options?: CheckImageCompareOptions | string)
This method compares the real-time screenshot of the target control with a specified reference image. If the difference between the two exceeds the preset tolerance threshold, the method will throw an exception and include a visual difference map (diffImage) in the error message to help you quickly locate the problem.
Tip: This method prioritizes using the screenshot of the virtual control itself for comparison; if the virtual control does not have an independent screenshot, it will crop the corresponding area from its parent control screenshot for comparison.
Reference Image Specification and Priority:
The checkImage method provides flexible reference image specification via the options parameter, with the following priority:
- Base64 Data: If the
optionsobject provides theimageproperty (Base64 encoded string or Node.jsBuffer), this data is prioritized as the reference image. - File Path:
- If the
optionsparameter itself is a string, it is treated as the path to the image file. - If
optionsis an object and theimageproperty is not provided butimagePathproperty is, the system loads the image file specified by this path as reference.
- If the
- Model Built-in Snapshot: If the
optionsparameter is omitted, or is an empty object, or only contains comparison options (likepixelPercentTolerance) without providing a specific image source (imageorimagePath), the reference image (snapshot) pre-saved for the control in the model file is used by default.
Parameters Detailed
Type:
CheckImageCompareOptions | string(Optional)CheckImageCompareOptionsConfiguration Object: When theoptionsparameter is an object, you can configure the following properties to specify the reference image source and adjust comparison accuracy and behavior:Image Source Specification:
image?: string | Buffer: (Optional) Provide Base64 encoded image data (stringtype) or Node.jsBufferobject. If this parameter is provided, the current image of the control will be compared with this image data.- Note: In Python environment, only passing Base64 encoded strings is supported.
imagePath?: string: (Optional) Provide image file path string. Ifimageproperty is not provided but this property is, the system loads and uses the image file specified by this path as reference.
Image Comparison Options:
colorTolerance?: number: (Optional)numbertype, defines the maximum difference tolerance allowed in color matching. Default value is0.1. Smaller values mean stricter color matching.pixelPercentTolerance?: number: (Optional)numbertype, defines the allowed maximum pixel percentage difference tolerance. For example, default value1means at most1%pixel difference is allowed.pixelNumberTolerance?: number: (Optional)numbertype, defines the allowed pixel count difference tolerance. If set to0, it means no difference in pixel count is allowed (unless overridden bypixelPercentTolerance).ignoreExtraPart?: boolean: (Optional)booleantype, specifies whether to ignore extra parts of one image during comparison. Default isfalse.
Returns:
Promise<void>: An asynchronous method that returns no value. If image comparison fails, an exception is thrown. The exception object contains adiffImagefield, which is PNG data ofBuffertype, representing the visual difference between two images. You can usetry...catchstatement to catch this exception and save the difference map as a local file for debugging and visual comparison.
Usage Example
The following example demonstrates multiple usages of checkImage method, assuming model.getVirtual("button_image") returns a virtual control object:
// Example Preparation: Get Base64 encoding of image (Demo only, get as needed in actual use)
let expect_image = await Image.fromFile("button1.png");
let image_data_base64 = await expect_image.getData({encoding: 'base64'});
// 1. Compare with Base64 image
await model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ image: image_data_base64 });
// 2. Compare with Base64 image, customize tolerance
await model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ image: image_data_base64, pixelPercentTolerance: 10 });
// 3. Compare with file path image (Pass path string directly)
await model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage("button1.png");
// 4. Compare with file path image (Via options.imagePath)
await model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ imagePath: "button1.png" });
// 5. Compare with file path image, customize tolerance
await model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ imagePath: "button1-error.png", pixelPercentTolerance: 5, colorTolerance: 0.05 });
// 6. Compare with model built-in snapshot, customize tolerance
await model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ pixelPercentTolerance: 0.5, colorTolerance: 0.05 });
// 7. Compare with model built-in snapshot (Use default tolerance)
await model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage();
// Add difference image to report
try {
await model.getButton("Underline").checkImage();
} catch (error){
this.attach(error.diffImage,"image/png")
}import base64 # Python example needs to import base64 module
# Example Preparation: Get Base64 encoding of image
base64_value = None
with open("button1.png", "rb") as f:
base64_value = base64.b64encode(f.read()).decode("utf-8")
# 1. Compare with Base64 image
model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ 'image': base64_value })
# 2. Compare with Base64 image, customize tolerance
model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ 'image': base64_value, 'pixelPercentTolerance': 10 })
# 3. Compare with file path image (Pass path string directly)
model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage("button1.png")
# 4. Compare with file path image (Via options['imagePath'])
model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ 'imagePath': "button1.png" })
# 5. Compare with file path image, customize tolerance
model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ 'imagePath': "button1-error.png", 'pixelPercentTolerance': 5, 'colorTolerance': 0.05 })
# 6. Compare with model built-in snapshot, customize tolerance
model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage({ 'pixelPercentTolerance': 0.5, 'colorTolerance': 0.05 })
# 7. Compare with model built-in snapshot (Use default tolerance)
model.getVirtual("button_image").checkImage()
# Save difference image locally
try:
model.getButton("Underline").checkImage()
except Exception as e:
with open("diff.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(e.diffImage)In the above examples, if the current visual representation of button_image control differs from the specified reference image (whether Base64 data, file, or internal snapshot) beyond the set tolerance (e.g., colorTolerance or pixelPercentTolerance), the checkImage method will throw an error indicating test failure.